What Is the PQRST Wave?
The PQRST waves are a fundamental concept in cardiology and emergency medicine, representing the electrical activity of the heart as recorded on an electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG). For healthcare providers, understanding the PQRST waves is essential for evaluating cardiac rhythms, identifying abnormalities, and making rapid decisions during life-threatening events. Accurate interpretation of these waves is critical in settings such as Basic Life Support (BLS), Advanced Cardiovascular Life Support (ACLS), and Pediatric Advanced Life Support (PALS), where timely interventions can directly influence patient survival.
The Components of the PQRST Wave
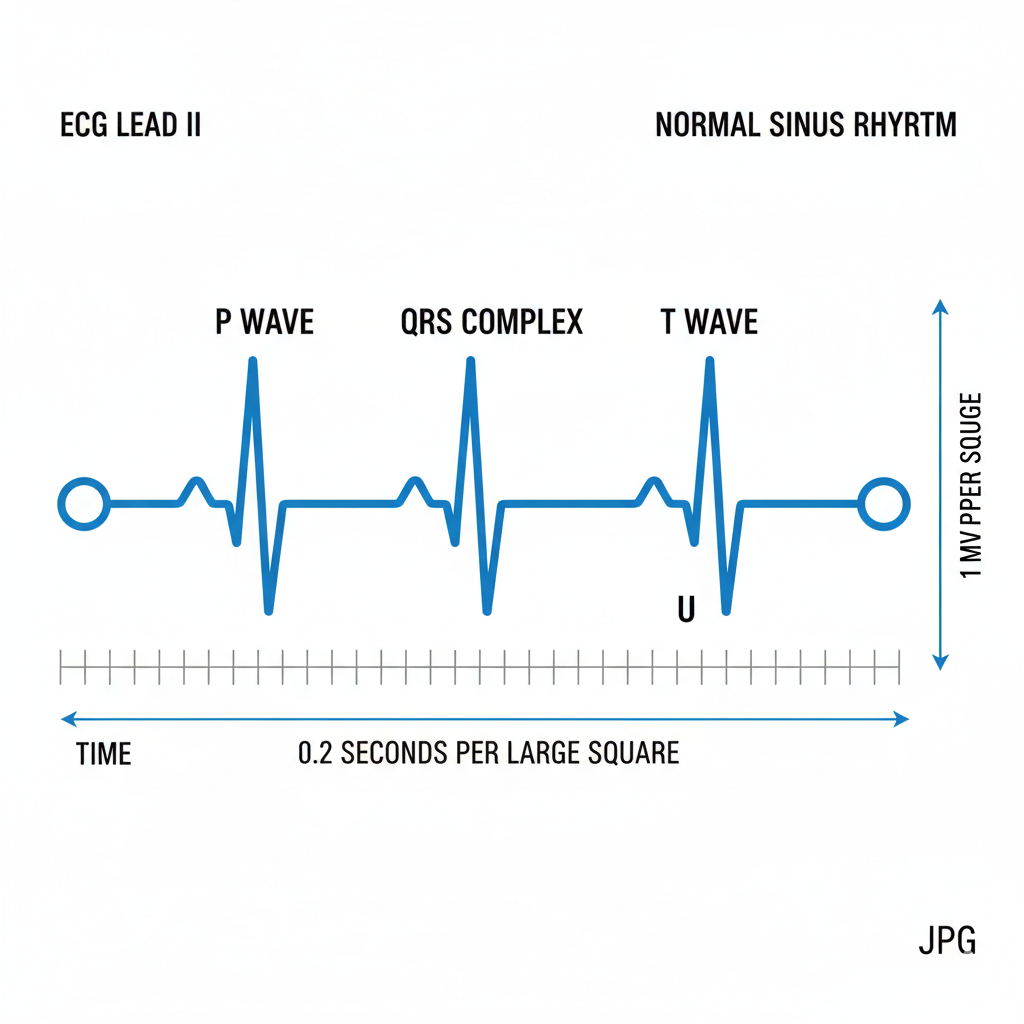
The PQRST waves are a graphical representation of the electrical impulses that govern heart contractions. Each component provides vital information about the heart’s conduction system and overall function. By analyzing these waves, healthcare providers can detect arrhythmias, ischemic changes, and conduction disturbances, allowing for informed clinical decisions. In emergency care, linking PQRST wave interpretation with ACLS and BLS protocols ensures that interventions, whether CPR, defibrillation, or medication administration, are appropriately timed and effective.
P Wave – Atrial Depolarization
The P wave represents atrial depolarization, signaling the electrical impulses that trigger the contraction of the atria. Normally, the P wave is smooth and upright in lead II, with an amplitude under 2.5 mm. Abnormalities in the P wave can indicate conditions such as atrial fibrillation, atrial flutter, or electrolyte disturbances. For example, absent P waves may suggest atrial fibrillation, while peaked or inverted P waves can indicate right or left atrial enlargement, respectively. Recognizing these variations is critical for early diagnosis and treatment planning.
QRS Complex – Ventricular Depolarization
The QRS complex corresponds to ventricular depolarization, which results in the pumping of blood to the lungs and the rest of the body. A normal QRS duration ranges from 0.08 to 0.10 seconds, with a consistent amplitude and morphology. Abnormalities in the QRS complex, such as widening, can signal conduction delays like bundle branch blocks or indicate ventricular tachycardia. Ventricular arrhythmias require immediate attention, often involving defibrillation and advanced life support interventions. Understanding QRS duration and morphology helps healthcare providers quickly identify potentially life-threatening situations.
T Wave – Ventricular Repolarization
The T waves represent ventricular repolarization, the phase in which the ventricles recover electrically in preparation for the next contraction. A normal T wave is upright in most leads, with a smooth, rounded shape. Abnormal T waves, such as inversion, flattening, or unusually tall peaks, may indicate ischemia, electrolyte imbalances, or other cardiac pathologies. For instance, hyperkalemia often manifests as peaked T waves, which requires urgent recognition to prevent progression to ventricular fibrillation or asystole.
PR Interval and ST Segment
The PR interval and ST segment provide additional diagnostic insight. The PR interval measures the time it takes for an electrical impulse to travel from the atria to the ventricles, normally lasting 0.12 to 0.20 seconds. Prolongation can indicate first-degree heart block, while shortening may signal pre-excitation syndromes. The ST segment is particularly important in detecting myocardial ischemia or infarction. Elevation or depression of the ST segment on an ECG requires immediate clinical attention, as it can indicate ongoing heart injury. These measures are integral to ACLS monitoring and inform rapid treatment decisions.
How to Read and Interpret the PQRST Wave
Reading and interpreting the PQRST waves involves a step-by-step approach. Providers should first ensure accurate lead placement and signal quality. Then, measure each interval and amplitude while observing rhythm regularity. Tools such as ECG monitors and feedback devices can assist in precise measurements, especially in advanced resuscitation scenarios. Common errors include misreading artifacts as arrhythmias, confusing fine VFib with asystole, or overlooking subtle ST changes. Practice and repeated exposure to ECG patterns enhance skill and confidence.
Clinical Significance of PQRST Wave Interpretation
The clinical significance of PQRST waves interpretation extends across BLS, ACLS, and PALS. In BLS, recognizing abnormal rhythms can guide the decision to initiate CPR or defibrillation. In ACLS, identifying shockable versus non-shockable rhythms determines medication timing and defibrillation protocol. Pediatric ECG interpretation under PALS requires awareness of age-related differences, as normal intervals and amplitudes vary in children. Quick and accurate rhythm recognition is often the deciding factor in patient survival.
Common ECG Abnormalities and What They Mean
Healthcare providers should also be familiar with common ECG abnormalities, including arrhythmias such as atrial fibrillation or ventricular tachycardia, ischemic changes reflected in ST elevation or depression, and heart block patterns ranging from first-degree to third-degree AV block. Understanding these abnormalities in the context of clinical scenarios allows providers to respond effectively, minimizing complications and improving outcomes.
Why Healthcare Providers Should Master PQRST Wave Interpretation
Mastering PQRST waves interpretation enhances clinical confidence during emergencies, supports faster diagnosis, and strengthens preparedness for certification exams in ACLS, PALS, and BLS. At CPR Jacksonville, FL, providers can gain hands-on experience interpreting PQRST waves, managing arrhythmias, and performing high-quality resuscitation in a stress-free, supportive environment. Courses are taught by American Heart Association-certified instructors and offer same-day certification cards, ensuring that participants leave prepared for real-world emergencies.
Conclusion
The PQRST waves provide essential information about the heart’s electrical activity, making them a cornerstone of cardiac assessment and emergency care. Understanding each component, recognizing abnormalities, and integrating these skills into life support protocols can save lives. Continuous education, practical training, and regular practice reinforce competence, allowing healthcare providers to respond confidently in critical situations. For those ready to advance their skills, CPR Jacksonville FL offers comprehensive courses in BLS, ACLS, and PALS, providing the knowledge and hands-on experience needed to excel in cardiac care and emergency response.